Table of Content
1. What is Isolator
2. Isolator Type
3. What is an isolation?
4. Utilization Category for an Isolator according to the type of load:
5. applications
What is Isolator
Isolator is a switching device which offers making and breaking of electric current in a circuit. Isolators are designed in compliance with IEC 60947-3 and performs below functions:
- Switching : ON / OFF
- Isolation
Generally used as a main switch or incomer inside a distribution board, an isolator does not offer any protection. It is used to completely disconnect the circuit from the electrical supply in order to achieve absolute isolation.
Isolator Type
Isolators are offered in Single Pole, Double Pole, Three Pole & Four Pole Variants in various current ratings such as 25A, 40A, 63A, 80A, 100A and 125A.
What is an isolation?
The question that arises now is what is meant by isolation and why is it required?
Isolation means complete disconnection of supply from the circuit. Isolator in OFF position must satisfy the conditions required for isolation as per IEC 60947-3.
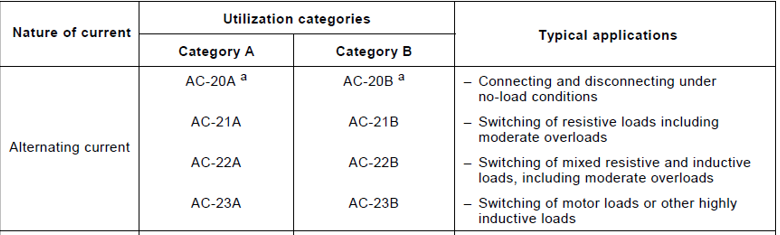
Utilization Category for an Isolator according to the type of load:
Applications
The isolators are suitable for residences, Offices, Buildings and Industries etc.